Get free consultation
Fill out the form and we will contact you
Canada, with its remarkable development and rich cultural diversity, has become an attractive destination for many people seeking opportunities for settlement, education, and work. In particular, many Vietnamese have chosen Canada as their second home. So, what makes this country so appealing, attracting a large number of tourists and new residents? In this article, let’s explore the distinctive features of Canada with Quốc Tịch Thứ Hai, through aspects such as national symbols, language, sports, human rights, and festivals.
The history of Canada’s formation spans five main stages, each marking important developments in the country:
Before the arrival of Europeans, the territory of Canada was already home to Indigenous peoples such as the Inuit and many other First Nations groups. These communities had developed rich cultures and had lived there for thousands of years.
John Cabot, an Italian explorer, is credited as the first European to reach the shores of Canada in 1497. Following him, explorers from France and England continued to explore and establish colonies. France established New France in eastern Canada, marking the beginning of European settlement in the region.
After numerous conflicts and wars, the French colonies in North America were seized by England. In 1867, through the British North America Act, Canada officially became the Dominion of Canada with its first four provinces: Ontario, Quebec, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia.
Canada gradually expanded its territory by adding new provinces and territories. The country became more autonomous through constitutional and legal amendments. In 1931, with the Statute of Westminster, Canada gained full autonomy and separated from the British political system, though it remained a part of the British Commonwealth.
In the 20th and 21st centuries, Canada developed into a modern industrial nation with a strong economy and a multicultural society. Today, Canada is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G7, and many other international organizations, playing an important role on the world stage.
Canada is located in the northern part of the North American continent, within the Americas, and spans between latitudes 41°N and 84°N, and longitudes 52°W and 141°W. With a total area of 9,984,670 square kilometers, of which 9,093,507 square kilometers is land and 891,163 square kilometers is water, Canada is the second-largest country in the world by area, only behind Russia.
Canada has the longest border in the world, stretching 202,080 kilometers, bordering the United States to the south and northwest, and it is surrounded by three major oceans: the Atlantic Ocean to the east, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and the Arctic Ocean to the north. The country also includes remote islands in the Arctic, such as Ellesmere Island, Baffin Island, and Victoria Island.
Canada's terrain is highly diverse, ranging from vast plains to majestic mountain ranges, from clear freshwater lakes to eternal glaciers. The geographic location of Canada not only has a profound impact on its natural environment but also plays a crucial role in shaping the country's unique economic, political, and cultural life..
Canada has three main climate types, divided by region:
Characteristic of the inland provinces and the Prairie region, the continental climate brings extremely cold winters, with daily average temperatures often reaching near -15°C, and dropping even further, sometimes below -40°C with wind chill. Snow can cover the ground for nearly six months of the year, and in some northern areas, snow can persist year-round.
Found mainly on the west coast of British Columbia, the moderate climate brings mild winters with rain. The average high temperature along the coast generally hovers around 20°C. In the inland areas and between the coastlines, summer temperatures can range from 25°C to 30°C, and sometimes exceed 40°C in certain regions.
Northern Canada is mostly covered by ice and frost. Climate change is causing the Arctic to warm at a rate three times faster than the global average. Since 1948, the average annual temperature on land in Canada has risen by 1.7°C, with the warming rate being especially high in the North and the Prairie provinces.
In Canada, the weather changes significantly with each season throughout the year:
Temperatures range from -7°C to 19°C, bringing warm weather and fresh scenery. Spring in Canada is the time when cherry blossoms and tulips bloom, especially in major cities like Toronto, Vancouver, and the Ottawa-Gatineau area. Parks like High Park and Stanley Park become ideal destinations to admire spring flowers and enjoy the fresh air.
Summer temperatures range from 20°C to 30°C, with areas like southern Ontario and Quebec generally being more humid, while other regions are drier and more comfortable. This is the season for festivals and outdoor activities such as camping, swimming, cycling, kayaking, and enjoying local specialties.
The average temperature is between 10°C and 12°C, with cool and dry weather. Fall in Canada is characterized by the changing colors of the leaves from green to yellow, red, and brown. It is an ideal time for picnics and hiking to enjoy the iconic red maple leaves.
Winter is the coldest season, with heavy snowfall and temperatures that can drop below -25°C in cities like Quebec City, Ottawa, Montreal, Winnipeg, and Edmonton. Despite the harsh weather, winter in Canada is full of life with Christmas festivals, and it is the season for popular winter sports like skiing, ice skating, ice hockey, and snowshoeing. The snowy landscape creates a dreamy beauty that attracts visitors.
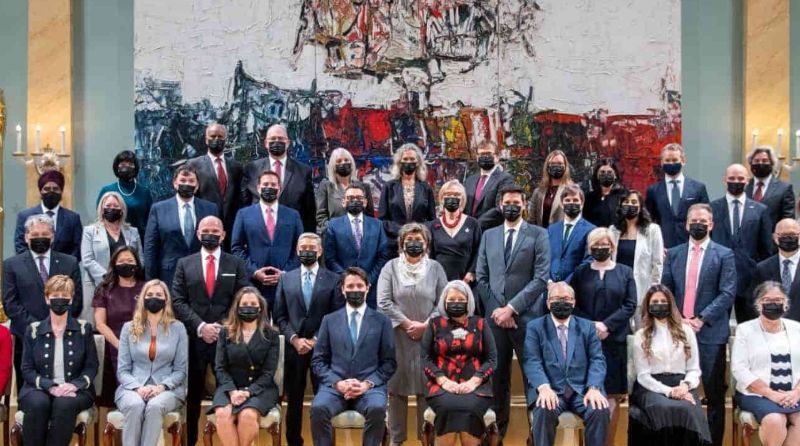
Canada is a constitutional monarchy, following a federal state model with a parliamentary democracy. Queen Elizabeth II holds the title of Queen of Canada and is the head of state, although she does not participate in day-to-day political affairs. Canada is divided into 10 provinces and 3 territories, each with its own government led by a premier and certain levels of autonomy.
The current Prime Minister of Canada is Justin Trudeau, the leader of the Liberal Party of Canada. He began his term in 2015 and was re-elected in 2019. Canada's political system consists of two main legislative bodies:
House of Commons: Responsible for legislating on federal matters.
Senate: Composed of senators appointed by the Governor General on the recommendation of the Prime Minister.
Canada’s constitution is a collection of documents and conventions that define the federal structure of the government and allocate powers between different levels of government. The current constitution, enacted on April 17, 1982, by Queen Elizabeth II, marked the end of Canada's dependency on the United Kingdom for constitutional amendments. The 1982 Constitution includes the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms, which protects the rights and freedoms of citizens.
Canada follows the principle of the rule of law, meaning everyone is subject to the law, and no one is above it. The judicial system of Canada includes independent and transparent courts responsible for resolving disputes and enforcing the law.
Although Canada’s political system is based on British law, it is also influenced by French legal traditions and Indigenous groups. Canada is a multicultural, multi-ethnic, and multi-religious country, where citizens are guaranteed freedom of speech, religion, equality, and democratic values.
Canada is a member of several important international organizations, including:
United Nations: Member since 1945.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO): Founding member since 1949.
Commonwealth of Nations: Member since 1931.
World Trade Organization (WTO): Member since its establishment in 1995.
Group of Seven (G7): Founding member.
Group of Twenty (G20): Active member.
In diplomacy, Canada maintains long-standing and positive relations with Cuba. Relations between the two countries began in the 18th century and were officially established in 1945. In 2021, Canada’s total exports to Cuba reached USD 225 million, while exports from Cuba to Canada were USD 23.8 million. Canada primarily exports products such as sulfur, wheat, and dry beans to Cuba.
Canada also shares a strong and close relationship with the United States, considering each other as close allies. The two countries collaborate extensively across various sectors, from defense to trade, particularly after signing the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and later the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). In 2022, the total bilateral trade between Canada and the United States reached nearly USD 1.3 trillion, demonstrating their robust trade cooperation.
Canada maintains a bilateral relationship with Vietnam, particularly in the economic sector. In 2015, Vietnam became Canada’s largest trade partner in the ASEAN region. In 2018, Canada and Vietnam signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP). In 2018, the total bilateral trade between the two countries reached approximately USD 6.4 billion.
Canada has a highly developed economy and is one of the seven leading industrialized nations in the world (G7). As a member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Canada ranked 9th globally in GDP with USD 1.736 trillion in 2020 and 15th in terms of purchasing power parity. Canada’s per capita income is USD 43,242.
It is expected that in 2023, Canada's GDP will reach approximately USD 2.118 trillion, reflecting a 22% growth compared to 2020. Canada’s main trading partners include the United States, China, and the United Kingdom, which together account for about 75% of the country’s total imports and exports.
Canada’s economy has a diverse structure and is mainly focused on three key sectors:
Service Sector: Contributing 70.2% to the national GDP, the service sector includes areas such as retail, business, education, healthcare, tourism, culture, and entertainment. This sector is the main source of employment, providing jobs for about 75% of the Canadian workforce.
Industrial Sector: Contributing 28.2% to GDP, the industrial sector includes activities such as mining, refining, and transporting oil, natural gas, electricity, and renewable energy sources. This sector employs around 280,000 people.
Agricultural Sector: Although it only contributes 1.6% to GDP, agriculture remains an important part of the economy, including crop production, livestock farming, fisheries, forestry, and food production. It generates employment for about 300,000 people.
However, Canada’s economy faces several challenges and risks, including global price volatility, international competition, reliance on the U.S. market, and delays in innovation and productivity improvements. To address these issues, the Canadian government has implemented policies to maintain economic stability, promote growth, create jobs, enhance the quality of life, improve competitiveness, expand trade, protect the environment, and reduce inequality.
Canada's economy is highly regarded for its human development, business freedom index, global peace index, and happiness index, proving to be one of the most advanced and successful economies in the world.
From the information above, it is clear that Canada is a unique, multifaceted, and captivating country. As a diverse mosaic of many different elements, Canada emerges as a vibrant and rich portrait. Upon setting foot in Canada, you will have the opportunity to experience a colorful and creative culture, where the blend of historical, geographical, and social factors creates a nation that is not only vast in size but also expansive in spirit and values. Canada attracts not only with its natural beauty but also with the diversity and openness of its people.
Fill out the form and we will contact you